Carbon dioxide hit highest level ever measured in the atmosphere in May
CO2 is the most abundant greenhouse gas.
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere in May 2021 hit the highest level ever measured, showing the global coronavirus pandemic did not decrease overall CO2 emissions despite pausing global economies for months.
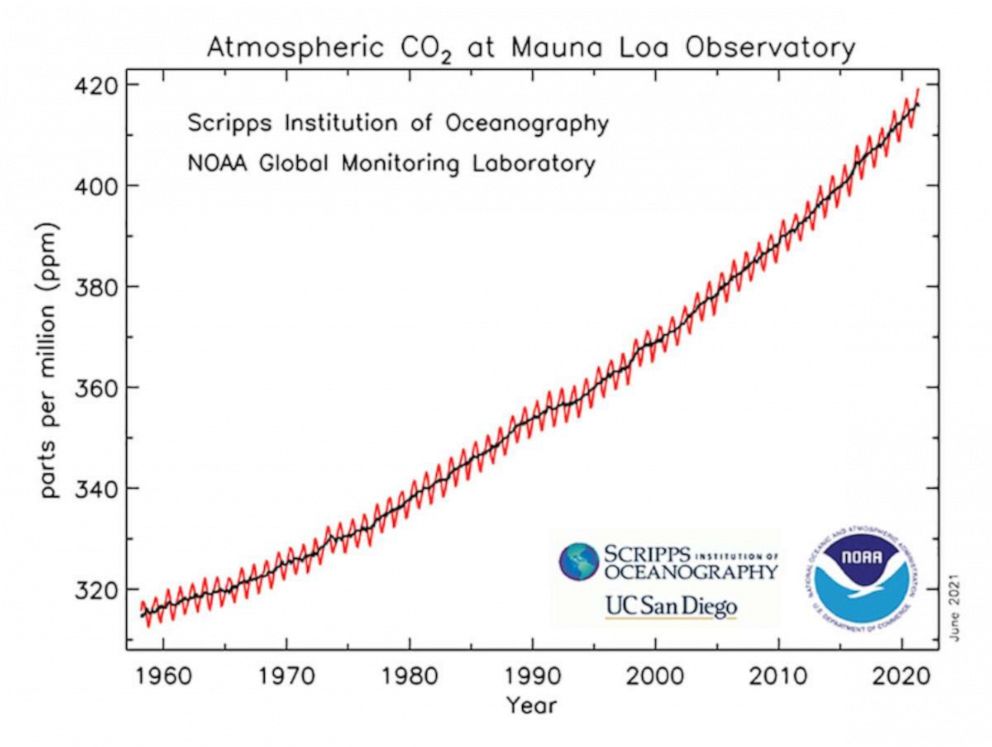
Atmospheric carbon dioxide hit a monthly average of 419 parts per million in May 2021, according to data from NOAA and the Scripps Institution of Oceanography released Monday.
"We are adding roughly 40 billion metric tons of CO2 pollution to the atmosphere per year," Peter Tans, senior scientist with NOAA's global monitoring lab, said in a statement.
"That is a mountain of carbon that we dig up out of the Earth, burn and release into the atmosphere as CO2 -- year after year. If we want to avoid catastrophic climate change, the highest priority must be to reduce CO2 pollution to zero at the earliest possible date."
NOAA and Scripps have been measuring CO2 levels from the Mauna Loa Observatory since 1958 and said that despite efforts to combat climate change and the economic pause from the pandemic level are continuing to rise.
Carbon dioxide is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, it is added from activities like burning fossil fuels to generate electricity, burning oil for transportation, industrial activity like manufacturing, agriculture and deforestation according to NOAA.
Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to increasing average temperatures and consequences like rising sea levels, ocean acidification and decreasing amounts of Arctic sea ice.

May is typically the highest CO2 measurement of the year as spring and summer in the northern hemisphere means more plants start to remove CO2 from the atmosphere in the following months.



